Here is what the discussion was please respond to each student with 100-150 words
Student 1
How much “statistical significance” do you need to feel confident in regression results? What could potentially affect those results and make them misleading, i.e., appear to be stronger than they are? Explain, discuss.
Two samples can be directly correlated, inversely correlated, or show little or no correlation. Closely correlated samples will show little scatter; the values will be close together. In contrast, samples that are not well-correlated will show significantly more scatter. The equation to determine the correlation coefficient, which is always a value between -1 and 1, is:
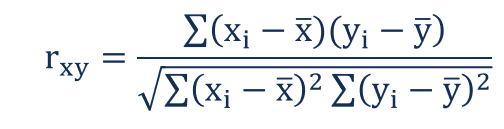
The significance of the correlation coefficient can be found by conducting a t test. The null and alternative hypotheses are constructed around the premise that the value is zero, indicating no correlation. A two-tail test is employed. The critical value of the test statistic is calculated and then compared to the t value listed for the given alpha level and relevant degrees of freedom/ number of tails for the test. If the calculated t value falls within the established range, the null hypothesis is not rejected. If the t value falls outside the established range, the null hypothesis is rejected and the researcher can determine that some correlation actually exists in the larger population from which the sample was taken. Furthermore, the p value can be found and the chances of a significantly different result can be calculated.
The aforementioned formula for calculating the t value is:
r√n−2/√1−r2
There is no single numerical significance that applies to all tests, although 95, 99, and 90% significance are most often used. The allowable error will determine which level is used. The correlation coefficient must be viewed in light of the results of the t test just described. The p value should also be considered. It is important to heed our authors’ admonition, for as Lind, Marchal, and Wathen (2019) state: “What we can conclude when we find two variables with a strong correlation is that there is a relationship or association between the two variables, not that a change in one causes a change in the other” (Lind, Marchal, & Wathen, 2019, p. 373).
When measuring correlation, it is important to consider all of the factors that might contribute to misleading results. A sample may indicate a trend that is not true for the larger population. Increasing the sample size can thus help to mitigate error. The sampling method might also not be the best for the task at hand. In this scenario, the sample size itself might be significant, but if it does not represent all segments of consequence, it may produce misleading results.
Reference
Lind, D. A., Marchal, W. G., & Wathen, S. A. (2019). Basic Statistics for Business & Economics (9th ed.) [E-book]. McGraw-Hill Education. https://player-ui.mheducation.com/#/epub/sn_0d33#epubcfi(%2F6%2F6%5Bdata-uuid- (Links to an external site.) 1214c94a9504baabf571613deb69c6a0%5D!%2F4%2F1:0) (Links to an external site.)
Student 2
Erica Burkett
Unit 6: Discussion
July 14, 2021
Direction:
How much “statistical significance” do you need to feel confident in regression results? What could potentially affect those results and make them misleading, i.e., appear to be stronger than they are? Explain, discuss.
Answer:
In the textbook, regression analysis is defined as “another method to examine a linear relationship between two variables that uses the basic concepts of correlation that provides much more information that will estimate the value of the dependent variable Y based on a selected value of the independent variable X” (Lind et al., p.381. 2019). The textbook also explains that “regression analysis provides two statistics to evaluate the predictive ability of a regression equation: the standard error of the estimate and the coefficient of determination” (Lind et al., p.395. 2019).
As it relates to the question, from my understanding the rule for regression analysis, the statistical significance would be 95% confidence level with the results. Two things that could make the results misleading if the outcome is either over or under specified, causing an error in the prediction widening the confidence level of the regression analysis.
Reference:
Lind, D. A., Marchal, W. G., Wathen, S. A. (2019). Basic Statistics for Business & Economics (9th ed., pp.381-395). New York, NY. McGraw-Hill Education.


0 comments