Q # 4 (a) Suppose a meter stick made of steel and one made of invar are the same length at 0°C. What is their difference in length at 39.5°C? The coefficient of thermal expansion is
12 ✕ 10−6/°C
for steel and
0.9 ✕ 10−6/°C
for invar.
mm
(b) Repeat the calculation for two 34.0-m-long surveyor’s tapes.
mm
——————————————————————————————————————————————
Q #5 The frames for a pair of eyeglasses have a radius of 2.06 cm at 20.0°C. Lenses with radius of 2.07 cm have to be inserted into these frames. To what temperature must the technician heat the frames to accommodate the lenses? The frames are made of a material whose thermal expansion coefficient is  10-4
10-4
°C
——————————————————————————————————————————————
Q # 6 Suppose a gas-filled incandescent light bulb is manufactured to have atmospheric pressure in it at 20.0°C. Find the gauge pressure inside such a bulb when it is hot, assuming its average temperature is 70.5°C and neglecting any change in volume due to thermal expansion or gas leaks.
atm
————————————————————————————————————————————————–
Q # 7 Suppose a gas-filled incandescent light bulb is manufactured from regular glass and with atmospheric pressure in it at 20.00°C. Its average temperature when hot is 62.66°C. Neglecting any change in volume due to thermal expansion or gas leaks, its gauge pressure is calculated to be 0.1456 atm. The actual final pressure for the light bulb will be less than calculated because the glass bulb will expand. What will the actual final gauge pressure be, taking this into account? The coefficient of volume expansion for regular glass is
27 ✕ 10−6/°C.
(Give your answer to at least four decimal places.)
atm
Is this a negligible difference compared to the pressure difference induced by the temperature increase? (Note: We define negligible as a difference less than 0.01 atm.)
—————————————————————————————————————————————–
Q # 8A high-pressure gas cylinder contains 60.0 L of toxic gas at a pressure of  107
107
(a) What is the final pressure in the tank, assuming a negligible amount of gas leaks while being cooled and that there is no phase change?
N/m2
(b) What is the final pressure if one-tenth of the gas escapes?
N/m2
(c) To what temperature must the tank be cooled to reduce the pressure to 1.00 atm (assuming the gas does not change phase and that there is no leakage during cooling)?
K
———————————————————————————————————————————————
Q #9 Two insulated cylinders A and B with volumes
VA = 3.0 m3
and
VB = 5.8 m3
contain chlorine gas at different pressures and temperatures. The cylinders are insulated (no heat is lost to or gained from the outside) and connected by a valve. Initially, the valve is closed and the gas in the two cylinders has the following values:
PA =  105
105
TA = 240 K,
PB =  105
105
TB = 560 K.
The valve is opened to allow the contents in the two cylinders to mix until the pressure equalizes.
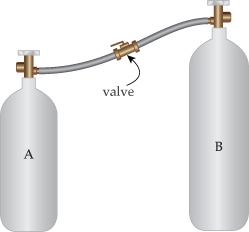
(a) Assuming there is no change in the temperatures of the containers themselves, determine the final temperature of the gas in the two cylinders. The atomic mass of chlorine gas is 35.4527 u.
k
(b) Determine the final pressure.
N/m2
———————————————————————————————————————————
Q # 10 Much of the gas near the Sun is atomic hydrogen. Its temperature would have to be  107
107 10-3
10-3
m/s
—————————————————————————————————————————-
Q # 11 Late on an autumn day, the relative humidity is 30.0% and the temperature is 20.0°C. What will the relative humidity be that evening when the temperature has dropped to 10.0°C, assuming constant water vapor density? Take the saturation vapor density at 20.0°C to be 17.2 g/m3 and at 10.0°C to be 9.40 g/m3.
%


0 comments