If you watch one of these and write up a brief response–what you liked, hated, learned, felt, thought, etc.–you’ll get some extra credit. Let’s say, write between 2 page (double spaced) and you’ll get 5 points on a major paper (whichever one needs it the most at the end).
I haven’t watched all of these, but they are related to what we’ve been discussing or I think it just might include some vital information. Here are the films you can choose from:The documentary is called heroine your are two write two pages about the documentary you learned about.
Heroin is an illegal, highly addictive drug processed from morphine, a naturally occurring substance extracted from the seed pod of certain varieties of poppy plants. It is typically sold as a white or brownish powder that is “cut” with sugars, starch, powdered milk, or quinine. Pure heroin is a white powder with a bitter taste that predominantly originates in South America and, to a lesser extent, from Southeast Asia, and dominates U.S. markets east of the Mississippi River.3 Highly pure heroin can be snorted or smoked and may be more appealing to new users because it eliminates the stigma associated with injection drug use. “Black tar” heroin is sticky like roofing tar or hard like coal and is predominantly produced in Mexico and sold in U.S. areas west of the Mississippi River.3 The dark color associated with black tar heroin results from crude processing methods that leave behind impurities. Impure heroin is usually dissolved, diluted, and injected into veins, muscles, or under the skin.
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | Heroin: /ˈhɛroʊɪn/ |
| Other names | Diacetylmorphine, acetomorphine, (dual) acetylated morphine, morphine diacetate, Diamorphine[1] (BAN UK) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | heroin |
| Dependence liability |
High[2] |
| Addiction liability |
High[3] |
| Routes of administration |
Intravenous, inhalation, transmucosal, by mouth, intranasal, rectal, intramuscular, subcutaneous, intrathecal |
| Drug class | Opioid |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | <35% (by mouth), 44–61% (inhaled)[4] |
| Protein binding | 0% (morphine metabolite 35%) |
| Metabolism | liver |
| Onset of action | Within minutes[5] |
| Elimination half-life | 2–3 minutes[6] |
| Duration of action | 4 to 5 hours[7] |
| Excretion | 90% kidney as glucuronides, rest biliary |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.380 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
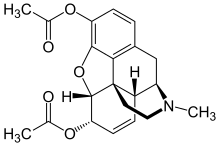
| Formula | C21H23NO5 |
| Molar mass | 369.417 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| (verify) | |
Heroin, also known as diacetylmorphine and diamorphine among other names,[1] is an opioid used as a recreational drug for its euphoric effects. Medical grade diamorphine is used as a pure hydrochloride salt which is distinguished from black tar heroin, a variable admixture of morphinederivatives—predominantly 6-MAM (6-monoacetylmorphine), which is the result of crude acetylation during clandestine production of street heroin.[3]Diamorphine is used medically in several countries to relieve pain, such as during childbirth or a heart attack, as well as in opioid replacement therapy.[8][9][10]
It is typically injected, usually into a vein, but it can also be smoked, snorted, or inhaled. In a clinical context the route of administration is most commonly intravenous injection; it may also be given by intramuscular or subcutaneous injection, as well as orally in the form of tablets.[11][3][12][13]The onset of effects is usually rapid and lasts for a few hours.[3]
Common side effects include respiratory depression (decreased breathing), dry mouth, drowsiness, impaired mental function, constipation, and addiction.[12] Side effects of use by injection can include abscesses, infected heart valves, blood-borne infections, and pneumonia.[12] After a history of long-term use, opioid withdrawal symptoms can begin within hours of the last use.[12] When given by injection into a vein, heroin has two to three times the effect of a similar dose of morphine.[3] It typically appears in the form of a white or brown powder.[12]
Treatment of heroin addiction often includes behavioral therapy and medications.[12] Medications can include buprenorphine, methadone, or naltrexone.[12] A heroin overdose may be treated with naloxone.[12] An estimated 17 million people as of 2015 use opiates, of which heroin is the most common,[14][15] and opioid use resulted in 122,000 deaths.[16] The total number of heroin users worldwide as of 2015 is believed to have increased in Africa, the Americas, and Asia since 2000.[17] In the United States, approximately 1.6 percent of people have used heroin at some point, with 950,000 using it in the last year.[12][18] When people die from overdosing on a drug, the drug is usually an opioid and often heroin.[14][19]
Heroin was first made by C. R. Alder Wright in 1874 from morphine, a natural product of the opium poppy.[20] Internationally, heroin is controlled under Schedules I and IV of the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs,[21] and it is generally illegal to make, possess, or sell without a license.[22] About 448 tons of heroin were made in 2016.[17] In 2015, Afghanistan produced about 66% of the world’s opium.[14] Illegal heroin is often mixed with other substances such as sugar, starch, caffeine, quinine, or other opioids like fentanyl.[3][23]
https://video.search.yahoo.com/yhs/search;_ylt=Awr…
Crime and Punishment (2018 documentary on Hulu)https://video.search.yahoo.com/yhs/search;_ylt=Awr…etflix



0 comments